Japanese cars are renowned for their reliability, and many owners of Japanese automobiles report being able to drive 200,000 or even 300,000 miles before any major repairs are needed. This is a testament to Japanese manufacturing and engineering, and is evidence that Japanese automobiles are among the most reliable on the road. Despite this, Japanese automobiles are still machines, and like all machines, they are prone to mechanical failure due to a number of different factors.
Common problems with Japanese cars include:
 Rust – Like all cars, Japanese auto bodies are prone to rust if not regularly maintained. Rust can cause cosmetic problems or can damage structural or mechanical components which can hinder the vehicle’s functionality.
Rust – Like all cars, Japanese auto bodies are prone to rust if not regularly maintained. Rust can cause cosmetic problems or can damage structural or mechanical components which can hinder the vehicle’s functionality.
Faded/Chipped/Cracked Paint – While Japanese automobiles are cut from a different cloth, the paint used on these automobiles is like all paint: subject to weather and damage. With age and time, as the paint is exposed to various elements, the color may fade and the paint itself may peel or chip.
Body Damage – Any car, especially used vehicles, are prone to scuffs, dents, or other unseen damage which can cause problems down the road. Be sure to visually inspect any used vehicle to ensure no hidden damages are present.
Suspension – Suspension systems will require maintenance, replacement, and ultimately repair as moving parts are exposed to forces throughout their working life.
Brakes – Brake systems will ultimately wear out as they transfer kinetic energy into heat to bring your vehicle to a complete stop. Replacing brake pads or shoes as they wear out will prevent damage to your rotors, which may need to be replaced.
These are just some of the more common problems that Japanese car owners may see with time and regular use, but is by no means a comprehensive list of potential problems. Japanese automobiles are reliable, but they are still machines, and these machines require maintenance and professional service from time to time. If you need auto repairs or maintenance on your Japanese vehicle, call Japanese Car Specialties! (949) 583-0811

 All vehicles need regular maintenance to keep functioning properly. Routine oil changes and tune ups are key, and maintaining your tires is equally as important. Here we walk through the safety and mechanical benefits of tire rotation.
All vehicles need regular maintenance to keep functioning properly. Routine oil changes and tune ups are key, and maintaining your tires is equally as important. Here we walk through the safety and mechanical benefits of tire rotation. There is a wide variety of reasons that your car may not start, but one of the most common is that your battery has died. Car batteries die for a handful of reasons including aging and overuse. Leaving electronically powered devices on while your car is not running absorbs electricity from your car’s battery, draining it and causing it to die. Luckily, there is a simple solution to this problem – jump starting your car.
There is a wide variety of reasons that your car may not start, but one of the most common is that your battery has died. Car batteries die for a handful of reasons including aging and overuse. Leaving electronically powered devices on while your car is not running absorbs electricity from your car’s battery, draining it and causing it to die. Luckily, there is a simple solution to this problem – jump starting your car. Most people don’t know the intricacies about how all of the myriad parts in their car function together. However, a basic understanding of some of the most important parts can prove beneficial in certain circumstances. If you understand the importance of your transmission, for instance, you’ll understand why a mechanic might tell you “Don’t let transmission damage compound”.
Most people don’t know the intricacies about how all of the myriad parts in their car function together. However, a basic understanding of some of the most important parts can prove beneficial in certain circumstances. If you understand the importance of your transmission, for instance, you’ll understand why a mechanic might tell you “Don’t let transmission damage compound”. With gas prices in an unpredictable flux, many drivers are going to great lengths to help their cars run more efficiently. While it is nearly impossible to get better mileage than your car is made for, there are many ways to help your car maintain its ideal mileage long term. Here we have compiled several methods to keep your mileage up and your car running smoothly.
With gas prices in an unpredictable flux, many drivers are going to great lengths to help their cars run more efficiently. While it is nearly impossible to get better mileage than your car is made for, there are many ways to help your car maintain its ideal mileage long term. Here we have compiled several methods to keep your mileage up and your car running smoothly. As a kid, your parents likely instilled in you the dangers of drunk driving. In their time, people didn’t know about its risks like they do today. However, our society has found other ways people increase their risk on the road, including driving sleep deprived. Sleep deprivation actually has a comparable risk to drunk driving; we’ll go over here why to avoid it.
As a kid, your parents likely instilled in you the dangers of drunk driving. In their time, people didn’t know about its risks like they do today. However, our society has found other ways people increase their risk on the road, including driving sleep deprived. Sleep deprivation actually has a comparable risk to drunk driving; we’ll go over here why to avoid it.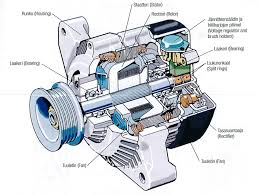 While your battery does supply your car with power, it can only do so for a short distance before it dies. Luckily, your alternator creates a charge from the kinetic energy supplied by your engine. It then recharges the battery as well as powers all of your car’s electronic equipment.
While your battery does supply your car with power, it can only do so for a short distance before it dies. Luckily, your alternator creates a charge from the kinetic energy supplied by your engine. It then recharges the battery as well as powers all of your car’s electronic equipment. For many people, when the subject of car parts comes up, their brain just shuts off; we’ve got mechanics to know that stuff for us. They seems so complicated that most people don’t see the point in trying to learn about them at all. In fact, in small doses, learning about how your vehicle functions can be entirely possible, even interesting. Why not begin now? We’ve created an overview of one of your car’s lesser known parts; the poly v belt.
For many people, when the subject of car parts comes up, their brain just shuts off; we’ve got mechanics to know that stuff for us. They seems so complicated that most people don’t see the point in trying to learn about them at all. In fact, in small doses, learning about how your vehicle functions can be entirely possible, even interesting. Why not begin now? We’ve created an overview of one of your car’s lesser known parts; the poly v belt.